Deep Vein Thrombosis
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit.
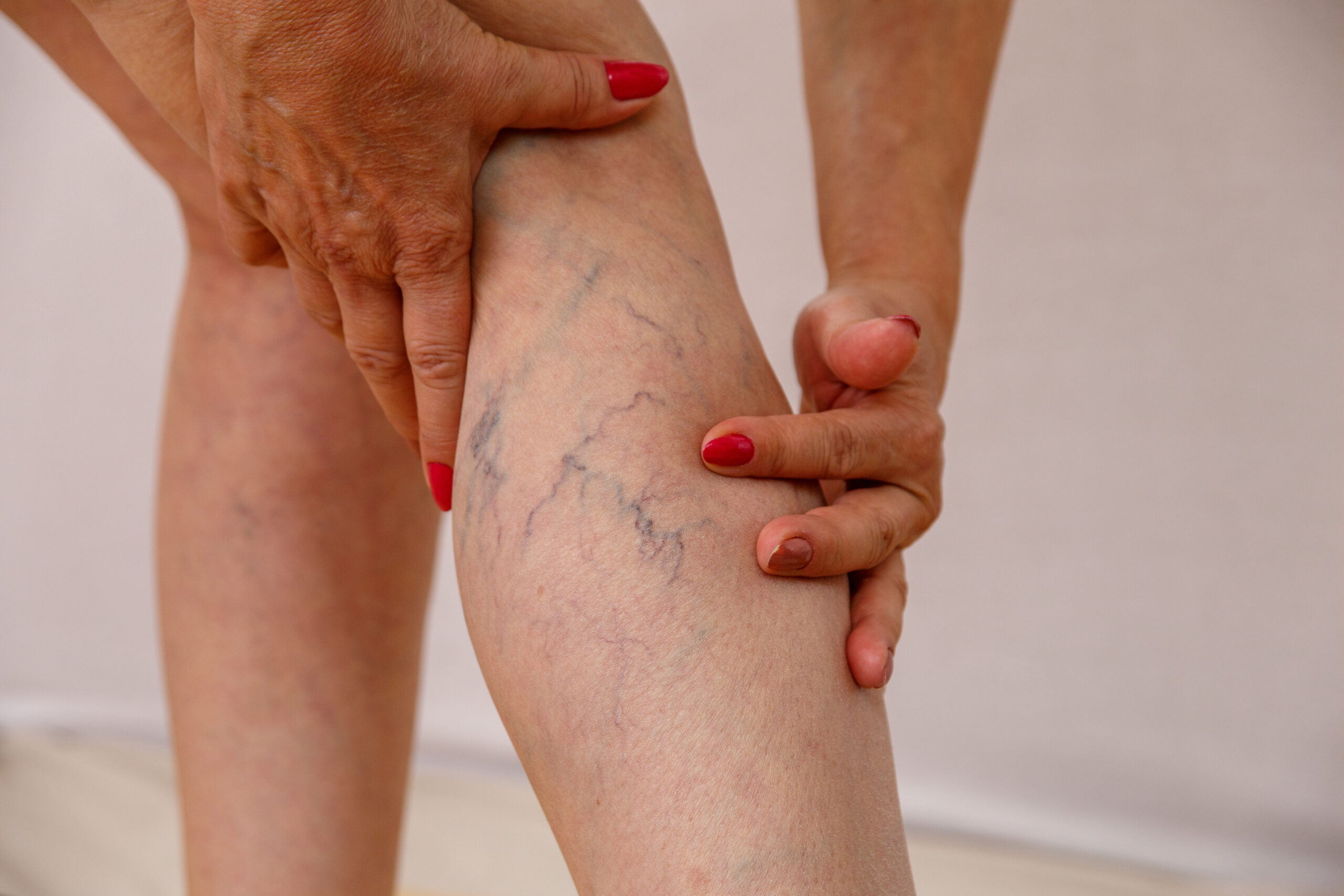
DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS
You’ve likely heard about blood clots, but have you considered the risks of deep vein thrombosis (DVT)? This condition, where blood clots form in the deep veins of your body, often in the legs, can be more than just a temporary inconvenience—it can potentially lead to serious health complications. If you’re experiencing leg pain or swelling or have risk factors for DVT, it’s time to consider visiting our Atlanta heart doctors for a thorough examination.
Deep vein thrombosis occurs when a blood clot forms in one of the deep veins in your body, most commonly in your legs. Think of it as a traffic jam in your blood vessels, blocking the normal flow of blood back to your heart. While your body naturally forms clots to stop bleeding when you’re injured, DVT clots form without serving a useful purpose and can be dangerous.
The danger lies not just in the clot itself but in what can happen if it breaks loose. A clot that travels to your lungs can cause a pulmonary embolism, a potentially life-threatening condition. Post-thrombotic syndrome, which causes chronic leg pain and swelling, can also result from DVT.
Symptoms of DVT can be subtle at first. You might notice swelling in one leg, particularly the calf. The affected area may feel warm to the touch and appear red or discolored. Many people experience pain or tenderness in the leg, which might feel like a cramp or soreness. In some cases, you might see visible surface veins. However, it’s important to note that some people with DVT don’t experience any symptoms at all.
By visiting our Atlanta heart doctors, you’re taking a proactive step towards protecting your cardiovascular health. Our cardiologists are experts in detecting and managing DVT. They can perform specialized tests like ultrasounds or blood tests to diagnose DVT quickly and accurately.
During your visit, you’ll receive personalized testing and treatment. Our doctors will assess your risk factors, including recent surgery, prolonged immobility, obesity, or certain medical conditions. To prevent the clot from growing and lessen the likelihood of future clots, your doctor will prescribe treatment that may include blood-thinning medicine. Your doctor can also prescribe lifestyle changes to help improve circulation and reduce your risk of future clots.
Don’t ignore leg pain or swelling, especially if you have risk factors for DVT. Schedule an appointment with our Atlanta heart doctors today to avoid overlooking this potentially serious condition. While DVT can be dangerous, with proper diagnosis and treatment, most people recover fully and can take steps to prevent future occurrences. Vascular health is an important part of your overall well-being, and our team is here to help you maintain healthy circulation throughout your body.
Read on for more information on deep vein thrombosis testing and treatment and how CVG provides comprehensive cardiac care.
Causes And Treatment Of Deep Vein Thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a condition where a blood clot forms within veins deep inside the body due to damage to the veins or the blood flowing through them too slowly. These blood clots can partially or completely block blood flow through the vein. Deep vein thrombosis typically occurs in the lower leg, thigh or pelvis, but they also can occur in other parts of your body including your arm, brain, intestines, liver or kidney
Causes Of Deep Vein Thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis is caused by the formation of a blood clot. There are many risk factors that can increase your chances of developing blood clots, such as genetic conditions, cancer and chemotherapy, injury, surgery, not moving for long periods of time, pregnancy, obesity, varicose veins, birth control pills, hormone therapy, COVID-19, or autoimmune diseases such as lupus, vasculitis, or inflammatory bowel disease.
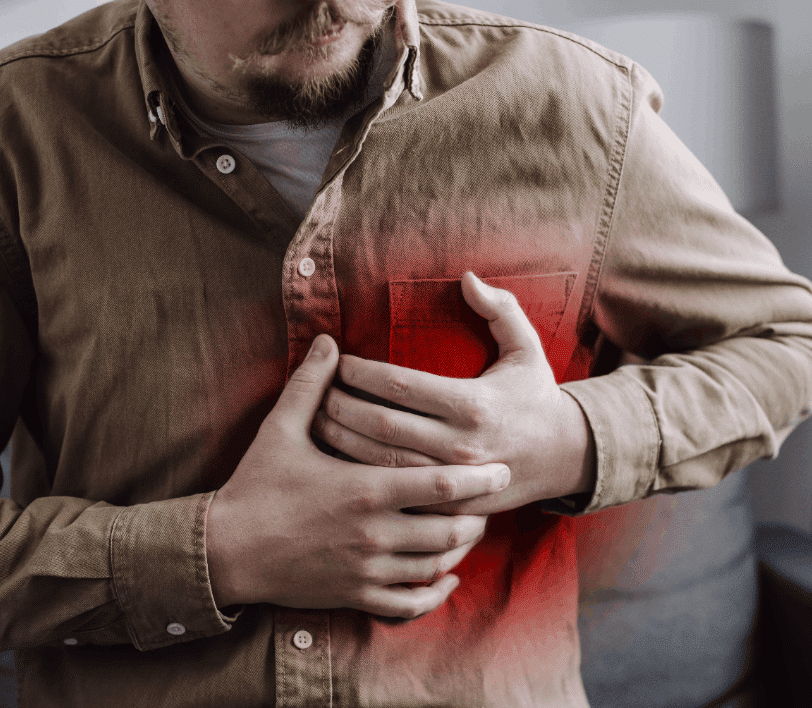

Testing For Deep Vein Thrombosis
To diagnose DVT, your doctor will begin by conducting a physical exam and asking about your symptoms and medical history. Your doctor will then conduct a series of imaging tests such as CT scans, MRIs, and MRVs. The most common test given to determine if you have deep vein thrombosis is known as a duplex venous ultrasound, which uses ultrasound waves to show blood flow and blood clots in your veins.
There is also an invasive test that can be given, known as venography, in which your doctor numbs the skin of your neck or groin and uses a catheter to inject a special dye into your veins to see if any blood clots are partially or completely blocking blood flow inside your veins. This test is rarely used now, as less invasive tests are available and can provide similar results, although sometimes it is necessary.
Treatment For Deep Vein Thrombosis
If you do require treatment for deep vein thrombosis, you will likely be prescribed medications such as anticoagulants (blood thinners) or thrombolytic drugs, or you may be told to wear compression stockings. You will also be given frequent blood tests to monitor the progression of your DVT.
In cases of severe deep vein thrombosis, you may require invasive procedures such as a surgical thrombectomy. This is typically only done when the clot that has developed is unusually large or is causing serious issues like tissue damage. This form of treatment can lead to certain complications such as infection, excess bleeding, or damage to the blood vessels, which is why surgery is only done in situations where other methods of treatment are ineffective.
Home remedies that can be done for deep vein thrombosis include a variety of exercises that work to increase the circulation of your blood. These exercises include knee pulls, foot pumps, and ankle circles. The main goals of DVT treatment are to keep the clot from getting bigger and spreading to other veins, prevent the clot from breaking off in your vein and moving to your lungs, lessen the risk of another blood clot developing, and .prevent long-term complications from the blood clot, such as chronic venous insufficiency.
Symptoms Of Deep Vein Thrombosis
DVT typically forms in the veins of your legs or arms, so many symptoms of DVT are associated with those areas. In some cases, people with deep vein thrombosis will experience no symptoms, or the symptoms will be very mild and not cause any concern.
Common symptoms associated with deep vein thrombosis include swelling of your leg or arm, pain or tenderness in the afflicted area, a feeling of warmness where the blood clot is located, skin that is red or discolored, veins near the skin’s surface being larger than normal, abdominal pain, severe headache, and in extreme circumstances, seizures.
Some people will have no idea they are experiencing deep vein thrombosis until the blood clot breaks off and travels to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism. Symptoms of this include chest pain, shortness of breath, cough with blood, lightheadedness and fainting.
Prevention Of Deep Vein Thrombosis
You can reduce your risk of developing deep vein thrombosis by using compression stockings, taking medications, and making lifestyle changes such as staying physically active, eating a healthy diet, staying hydrated, and avoiding tobacco products. If there are periods where you are sitting still for long amounts of time, such as at an office job or on long flights, stand up and walk for a bit every half hour. Moving around increases blood flow and helps to prevent blood clots from forming.
Why Choose CVG?
At CVG, our cardiologists offer extensive experience caring for patients using state-of-the-art techniques. Their compassion adds so much to your care because our doctors understand how heart issues can affect you physically and take an emotional toll. Trust is the #1 factor in the doctor/patient relationship. You can trust your CVG cardiologist with every aspect of heart care.
Board-certified Doctors
CVG’s twenty board-certified heart doctors will guide you through your healthcare journey with the utmost compassion and individual attention. We aim to provide you with state-of-the-art cardiac care that includes the full spectrum of services, from testing to diagnosis and treatment. The doctor/patient relationship is built on trust. Through our combined efforts, we can conquer any challenge that comes our way.
Invasive therapies may also treat an abnormal heart rhythm, such as electrical cardioversion, which sends electrical impulses through your chest wall and allows your normal heart rhythm to restart, or catheter ablation, which disconnects the abnormal rhythm’s pathway. Suppose your doctor determines that electrical devices are the best course of action. In that case, you may be given a permanent pacemaker, an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD), or biventricular (B-V) pacemakers and defibrillators.
Related Conditions:
Top Conditions:
Call to Schedule an Appointment
Invasive therapies may also be used to treat an abnormal heart rhythm, such as electrical cardioversion which sends electrical impulses through your chest wall and allows normal heart rhythm to restart, or catheter ablation which disconnects the pathway of the abnormal rhythm. If your doctor determines that electrical devices are the best course of action, you may be given a permanent pacemaker, an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD), or biventricular (B-V) pacemakers and defibrillators.
How CVG Can Help
Locations That Treat Arrhythmias

Office Suwanee
1120 Peachtree Industrial Boulevard Suite 208 & 209 Suwanee, Georgia
- 7706379247
- 7702908084





