Comprehensive Heart Care
Welcome to our dedicated page on Cardiovascular Health and Patient Services! Discover comprehensive information and top-notch services tailored to treat specific heart conditions and support your health journey. Our experienced team of cardiologists is ready to assist you anytime.
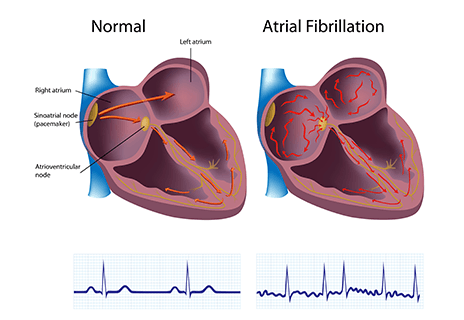
Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation (AFib) is one of the most common irregular heart rhythms afflicting all Americans. This occurs in about 5% of the population annually. This is a treatable condition. Once diagnosed, the patient should undergo outpatient heart tests to establish the frequency and the possible cause of the atrial fibrillation. The biggest danger of atrial fibrillation is a stroke. Long term atrial fibrillation can lead to heart failure. The most common causes of atrial fibrillation are high blood pressure and sleep apnea. There are multiple other causes.
Catheter Ablation
This is a minimally invasive procedure used to attempt to eliminate irregular heart rhythms. The most common irregular heart rhythm this is utilized for is atrial fibrillation. During the procedure, a catheter is inserted into the heart to map out the area causing the irregular heart rhythm. Once the area has been isolated, another catheter is used to create scar tissue in this area to disrupt the abnormal electrical signals causing the irregular heart rhythm. Treatment can be effective in potentially curing the patient, reducing the chance of sudden death and improving quality of life.
Electrical Cardioversion
This treatment is used to convert a patient’s irregular rhythm to a normal sinus rhythm by administering an electrical shock to the heart. It is most commonly used for patients with atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter. The patient is placed under anesthetic. The patient’s heart is synchronized with the machine. Once completely sedated, a synchronous shock is conducted via electrical pads which have been placed on the back and front of the patient’s chest. This procedure is usually done as an elective procedure where the patient is discharged approximately an hour after the procedure. Cardioversion can also be performed in emergency situations when a patient has a cardiac arrest and has an irregular heart rhythm that is able to be shocked.
Electrocardiogram
Electrocardiogram (EKG) is the most basic heart test which evaluates the electrical conduction of the heart. It can be used to diagnose abnormal heart rhythms, potential heart attacks and possible heart enlargement. It is also used to monitor certain medications that can affect the heart. The EKG is performed by medical assistants or technicians. Electrodes are attached in certain positions on the patient’s chest, arms and abdomen. The machine then computerizes the electrical activity of the heart and prints out an EKG. This is done while the patient is at rest.
Electrophysiology Study
Electrophysiology is the study of the electrical system of the heart. It is a very sophisticated test to map out the electrical activity of the heart. It is used to determine any abnormal electrical conduction pathways in one’s heart which may predispose or cause irregular heart rhythms. The procedure is done under moderate sedation or sometimes general anesthesia.
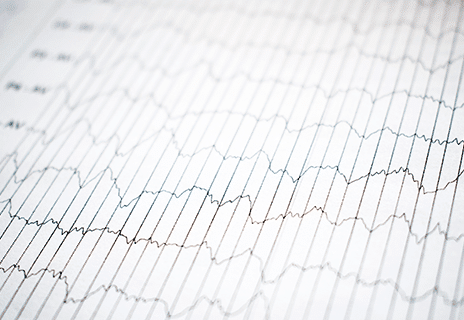
Expert Insights On Cardiac Catheterization
This test is used to look for blockages inside the blood vessels that supply blood and oxygen to one’s heart. It is also used to measure pressures inside your heart and lungs. This also quantifies the amount of blood flow down your heart vessels.
The test is done under moderate sedation as well as local anesthetic administered to the access site. The access site is either the blood vessel that brings blood to one’s hands or legs.
If one finds a significant narrowing or blockage in a heart vessel, this can be fixed under most circumstances while the patient is still on the table utilizing a metal scaffolding object called a stent. If one has too many blockages, the patient may need bypass surgery. This is done as a separate procedure by cardiothoracic surgeons.
The procedure itself may take 15 to 20 minutes or longer if stents are required. The patient is then transferred to the recovery unit for monitoring. The patient is then either discharged home with instructions or admitted depending on his or her condition.
This is the same procedure that patients have in the acute setting if they present to the emergency room having a heart attack.
Heart Structure Tests
The most common test is called an echocardiogram. This test utilizes sound waves to outline the structures of the heart. This includes the heart muscle, chambers, valves and large blood vessels which originate from the heart. These large vessels supply blood to the body. The one blood vessel is called the aorta. There is another large blood vessel that supplies blood to the lungs called the pulmonary artery. This test does not look at the blood supply of the heart. Echo can also measure the contractility of the heart and the pressures inside the heart. This test is performed by placing the ultrasound probe in different places on the patient’s chest. It is done by an ultrasound technologist. There is a more invasive way of performing an echocardiogram, if required. This is called a transesophageal echocardiogram. This allows one to capture 2D and 3D images of the heart. Chest X-ray is a screening test that can be used to tell whether you suspect heart enlargement. It can also tell whether the patient has fluid on the lungs, called heart failure.
Hypertension
This is the most common cardiac condition in the world. It is present in about 50% of adults in the USA. It means that your blood pressure is elevated. This is most commonly inherited. Blood pressure (BP) is measured using a cuff called a sphygmomanometer. BP should be measured while the patient is at rest and preferably seated with your feet touching the ground. There are two readings that are obtained. The top number is called the systolic pressure and should be less than 120. The bottom number is the diastolic pressure and should be less than 80. Treatable blood pressure with medication is above 130 / 80.

Stress Tests
A stress test is performed in two different ways. One can either exercise with the use of a treadmill or a bicycle. If exercise is not possible, a medication simulated stress test can be performed.
Stress tests are primarily used to screen for a potential lack of blood supply to the heart. The heart works on supply- demand. If there is a mismatch this can sometimes be seen by the EKG pattern changing on a stress test. The routine exercise treadmill test is not 100% accurate. It is about 60% sensitive.
There are more sophisticated stress tests utilizing imaging that increase the accuracy of the tests. A picture is taken of the patient’s heart at rest. The patient then either exercises on a treadmill or is given medication to simulate exercise. A second set of images is then obtained. These are the stress images. One compares the resting images to the stress images. If there is a lack of blood to the heart, there will be a deficiency in that area visualized on the stress image. There may also be a deficiency in the contractility of the wall of the heart in their territory. These tests are 80 to 85% accurate.
Watchman Implant Procedure
Atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter are irregular heart rhythms that predispose certain patients to forming a blood clot in the left upper chamber of the heart. This blood clot forms in an area of the chamber called the left atrial appendage. If a patient is deemed at risk for forming a blood clot from either of these rhythms, they are then placed on a blood thinner. However, not everyone is a candidate for a blood thinner. They may be at risk for bleeding, be a high risk for falls which increases the risk of bleeding post trauma or have other conditions where blood thinning medication is contraindicated.
There is now an alternative to blood thinning medication. The procedure is called a left atrial appendage closure. A device is used to cap off the left atrial appendage. This obviates the need for long term use of blood thinning medication. There are currently two different types of devices available that can be utilized for this procedure. The device is inserted via a vein in the groin called the femoral vein. Ultrasound guidance is used to position the device in the left atrial appendage. The patient is under general anaesthetic for the procedure. It is usually done as an outpatient procedure.
Cardiac CAT Scan
There are two different ways the CAT scan can be utilized in heart testing. There is a test called a coronary calcium score. This test does not involve the use of iodine based dye. It is a specialized X-ray of the heart and the chest used to detect the amount of calcium deposited in the walls of the blood vessels that supply blood to the heart. The layman’s term for coronary deposits in the blood vessels around the heart is called “hardening of the arteries”. This test does not look for blockage inside the blood vessels. It is designed to screen for the risk of developing blockage inside the blood vessels in one’s future. The higher the score the higher the risk and an ideal score is zero. This test also allows measurement of the main blood vessel leading out of the heart and supplying blood to the body, called the aorta.
The second modality of CAT scan utilization is to visualize potential blockage inside the blood vessels supplying blood to the heart. This is performed by injecting an iodine based dye into an arm vein of the patient. The dye is then tracked down the blood vessels of the heart while images are taken. Of note, these blood vessels are located on the outside of the heart. Blood supply of the heart occurs from the outside of the heart inwards. It spreads through the muscle wall of the heart. If significant blockages are visualized, there is a separate modality that allows one to estimate the amount of blood flow down the vessels. No additional images are required for the second part of this test. This test is considered to be 80 to 85% accurate in diagnosing a blockage in a blood vessel around the heart.

Cardio – Oncology
Heart disease and cancer account for about 50% of deaths per year in the USA. There are more and more successful treatments being developed to fight cancer. These include different chemotherapy agents as well as immune targeted therapeutic agents. While these are potentially curative agents to the patient, some of them are harmful to the heart. This has necessitated a new partnership to blossom between cardiologists and oncologists. This is designed to best treat and monitor the patients who have cancer who are required to take these drugs. We utilize EKG’s, echo, cat scan and cardiac MRI to help design and direct and navigate the patient through their treatment.
The symptom complex for patients undergoing treatment is essentially the same for any patients suffering from a potential heart condition. The most common symptoms are shortness of breath, chest pain, palpitations and leg swelling.
Cardio – Obstetrics
This is a specialized field of medicine designed for women of childbearing age who have pre-existing heart conditions or develop heart conditions during pregnancy. Unfortunately, some of the most common medications used to treat high blood pressure and other heart conditions cannot be used in pregnancy due to the potential danger to the embryo. It is vitally important that your obstetrician is aware of any medication that you’re taking. This field allows your doctors to direct and navigate you through your pregnancy and beyond. Preeclampsia places you at increased risk for cardiac disease in the future.

Cardiac MRI
MRI has become an excellent modality to image heart structures. It does utilize an imaging material called gadolinium. This is not damaging to the kidneys and can be used in patients with kidney disease who cannot undergo CAT scans with the use of iodine based dye. Cardiac MRI is valuable in detecting and diagnosing congenital heart disease. It can also be used to diagnose a condition called amyloidosis and potential cancers involving the heart.
We suspect cardiac MRI will become more and more useful in the future.
Find the care that you need.



